A Complete Beginner-Friendly Guide
The topic of cryptocurrency is no longer specialized. With thousands of digital assets, each with a distinct function, it has developed into a huge worldwide industry. Knowing the main types of cryptocurrencies is crucial, regardless of your familiarity with them. The primary categories of cryptocurrencies—Bitcoin, altcoins, stablecoins, and utility tokens—will be discussed in this blog. We’ll also address frequently asked questions and conclude with a quick test to gauge your comprehension.

Why Understanding Crypto Types Matters
Before investing or using digital assets, you should know:
- What each kind of cryptocurrency is intended for,
- their actions in the market
- The advantages and disadvantages
- The reasons behind their existence In a room full of thousands of coins and tokens, this information helps you make wise choices and stay clear of confusion.
Bitcoin (BTC): The First and Most Valuable Cryptocurrency
The entire cryptocurrency industry was founded on Bitcoin. It introduced the concept of a decentralized, peer-to-peer financial system when Satoshi Nakamoto launched it in 2009.
Key Features of Bitcoin
- Digital Store of Value: Due to its small supply (21 million coins), it is frequently compared to gold.
- Highly Decentralized: Bitcoin is resistant to censorship because no single organization controls it.
- Secure Proof-of-Work System: Miners use cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions.
- Worldwide Acceptance: Millions of users, payment processors, and retailers all accept Bitcoin.
Why Bitcoin Matters
Some refer to Bitcoin as the “digital gold standard.” In the quickly changing world of cryptocurrencies, it stands for security, scarcity, and dependability.

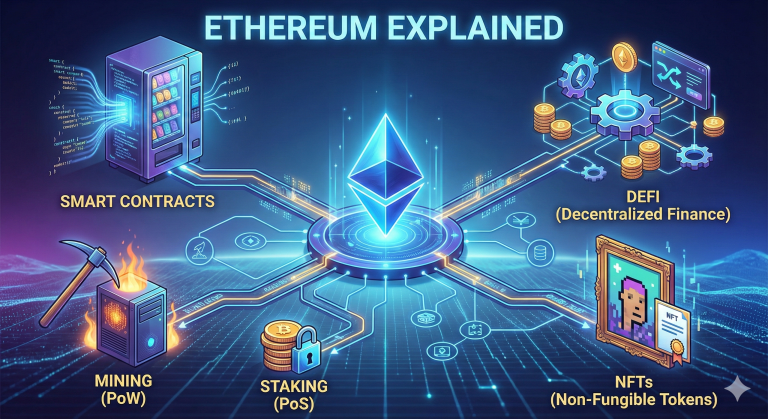
Altcoins: All Cryptocurrencies Other Than Bitcoin
The term “altcoin” simply means “alternative coin.” These are cryptocurrencies developed after Bitcoin, frequently with the goal of improving or expanding the technology.
- Popular Alternative Coins
Ethereum (ETH) is the foundation of decentralized applications and smart contracts. Solana (SOL) is known for its ultra-fast transactions. Cardano (ADA): Based on academic research and peer-reviewed technology. XRP: Designed for rapid and low-cost international payments.
- What makes altcoins unique?
Altcoins can offer:
- Faster transaction speeds.
- More flexibility
- Smart Contract Capabilities
- Various consensus mechanisms (proof of stake, delegated PoS, etc.)
- Use cases include gaming, AI, NFTs, DeFi, and identity systems.
Some altcoins are experimental, while others are the foundation of major blockchain ecosystems.

Stablecoins: Crypto Designed to Stay Stable
Crypto markets are notoriously volatile, but stablecoins provide a calming presence in the midst of the upheaval.
- Examples of stablecoins.
- USDT (tether)
- USD Coin (USDC)
- DAI
- How Do Stablecoins Work?
Most stablecoins are tied to a stable asset, such as:
- The US Dollar
- A basket of currencies.
- Commodities (such as gold)
- Stablecoins are important for:
- trading (without changing back into fiat currency)
- Protecting funds during market declines
- Transferring money globally at cheap fees
- Enabling DeFi lending, borrowing, and yield farming.
Utility Tokens: The Fuel That Powers Crypto Ecosystems
Some cryptocurrencies exist as tools within a certain platform, rather than as money.
- Popular utility tokens.
BNB: Used to trade discounts and ecosystem utilities on Binance. LINK: Supports Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network. UNI: Used for governance and rewards in Uniswap.
- What Utility Tokens Do
- Pay the transaction fees.
- Run smart contracts.
- Unlock the premium platform features.
- Vote on the governance proposals.
- Offer incentives to network users and validators.
Utility tokens act as digital fuel, keeping decentralized applications running.